Local Storage seems to be disabled in your browser.
For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Local Storage in your browser.
Testing of metallic valves
Different standards may be referred to regarding metallic valve testing and leakage rating. Two main standards are most commonly used :
EN 12266-1 and API 598. Where any of those 2 standard is specified as a normative reference in a product, its performance shall be considered according to the requirements of that standard.
EN 12266-1
Industrial valves - Testing of metallic valves - Part 1: Pressure tests, test procedures and acceptance criteria - Mandatory requirements
The EN 12266-1 specifies the mandatory test requirements, test procedures and acceptance criteria for production testing of industrial valves made of metallic materials. Safety devices are not in the scope of the EN 12266-1. The prescribed tests may also be used as type tests, or acceptance tests.
The following requirements are considered : Shell resistance, shell tightness, seat tightness and closure resistance. The Annex A of the standard defines the test procedures and acceptance criteria.
1 - Test pressure & medium
- Shell resistance (P10), shell tightness (P11) and closure resistance (P20): test pressure = 1.5 x PS (max. allowable pressure at ambient temp.). Shell resistance & tightness must be tested with liquid unless otherwise agreed by the parties.
- Seat tightness (P12): the test pressure shall be at least 1.1 x PS (max. allowable pressure at ambient temp.). If the test medium is a gas,
the test pressure shall be the lower between 1.1 x PS and 6 bar (±.1 bar).
2 - Duration of test (Tables A.2 & A.4 - Minimum duration of test)
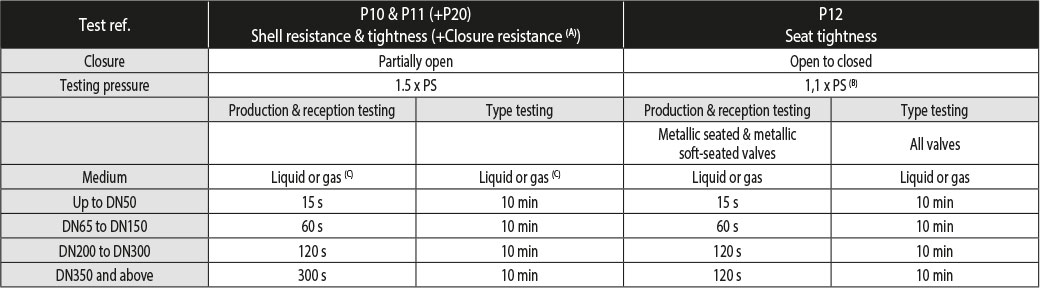

(A) Check the pressure resistance of the closure if the valve is used as the sole means of isolation between the contents of a pressure equipment
and the downstream part not designed to withstand the upstream pressure.
(B) If the test medium is a gas, the test pressure shall be the lower between 1.1 x PS and 6 bar (±1 bar).
(C) Shell resistance must be tested with liquid unless otherwise agreed by the parties.
3 - Acceptance criteria
- For the shell resistance, shell tightness and closure resistance tests:
- Whether the test is performed with a liquid or a gas, no visible leakage is allowed.
- For the seat tightness test, the selection of rates A to G is specified in the corresponding valve product standards.
- The leakage rates measured during the test period shall not exceed the rate specified in the following table (Table A.5 - Maximum allowable seat leakage for each leakage rate - in mm3/s) :


Note 1 - Leakage rates apply only for discharge at room temperature.
Note 2 - "No visually detectable leakage" means no visible seepage or formation of drops or bubbles.
If leakage rate measurements are made by automatic means, they must be qualified by the manufacturer's quality system.
API 598
Valve Inspection and Testing
1 - Scope
The API 598, from the American Petroleum Institute, provides industry standards for valve ratings and valve leakage allowance. The standard
is currently in the 10th edition (2016). It covers inspection, examination, and pressure test requirements for resilient-seated, nonmetallic-seated, and metal-to-metal-seated valves of the gate, globe, plug, ball, check, and butterfly types.
API 598 specifies the following tests and examinations :
- Shell resistance tests to validate the pressure containing structures of the valve.
- Backseat tests to verify the leakage through the sealing of the stem.
- Low-pressure & high pressure closure tests to verify the leakage through the closure mechanism.
2 - Pressure tests (Tables 1 & 2 - Pressure tests according to valve type)
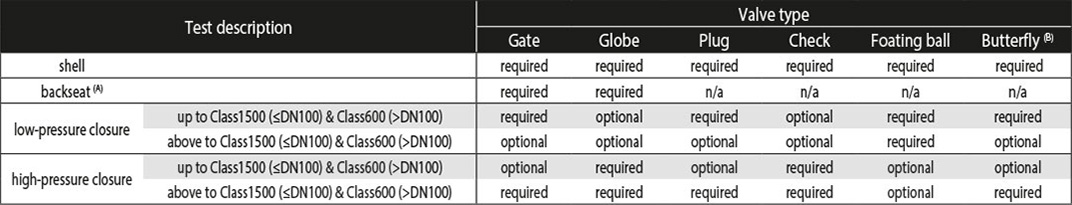

(A) The backseat test is required for all valves, except for bellows seal valves, that have the backseat feature. / (B) Also applies to trunnion mounted ball valves.
The test medium shall be air, inert gas, kerosene, water (or a noncorrosive liquid with a viscosity no higher than that of water) at temperature between 5°C and 50°C. The test pressures depend on the valve type, the pressure class and the DN of the valve according to tables 3 & 4.
3 - Duration of test (Tables A.2 & A.4 - Minimum duration of test)
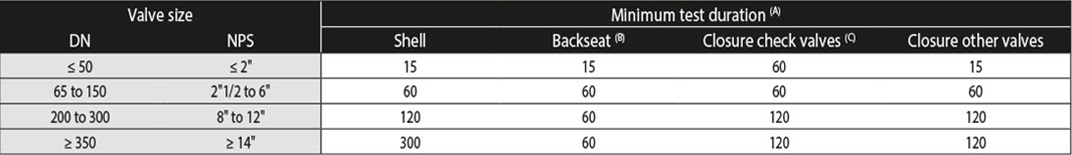

(A) In seconds. The test duration is the period of inspection after the valve is fully prepared and is under full pressure. / (B) For valves with backseat feature. /
(C) API 594.
4 - Acceptance criteria
- For the shell and backseat tests:
- Whether the test is performed with a liquid or a gas, no visual detectable leakage is permitted.
- For the low-pressure closure test, the table 6 defines the maximum allowable leakage rates for closure tests.
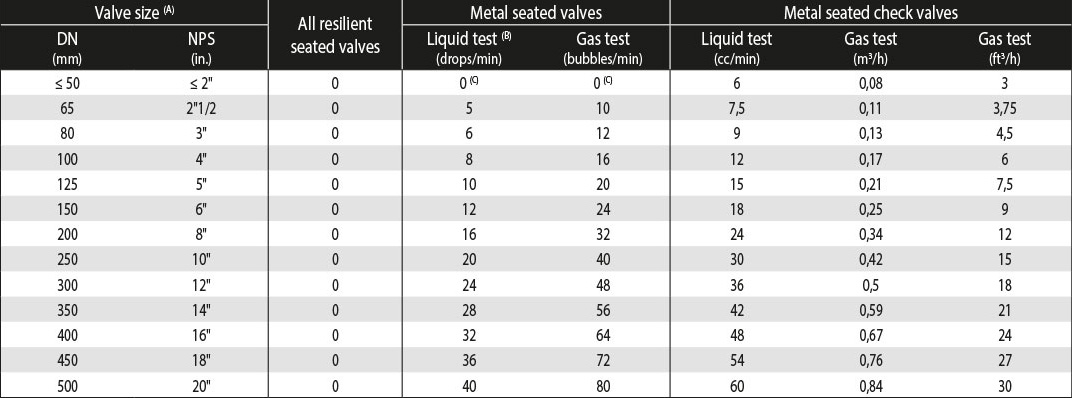

(A) For valve size above DN500 (NPS20), please refer to the API 598 standard for rates values. / (B) For the liquid test, 1 mL is considered equivalent to 16 drops. / (C) There shall be no leakage for the minimum specified test duration (see Table 5). For liquid test, 0 drop means no visible leakage. For gas test, 0 bubbles means less than 1 bubble.
