Local Storage seems to be disabled in your browser.
For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Local Storage in your browser.
INDUSTRY
The industry is a vital sector of the global economy, encompassing a wide range of production and distribution activities. Among the many companies contributing to this sector, Syveco is a stockist in distributing industrial valves and fittings for industrial applications.
Fluids are everywhere in the industry. They are present as production in the strict sense of the word but also as fluids in secondary circuits or utilities. Managing these fluids requires various equipment, such as valves and fittings. Syveco occupies a key position in the industrial landscape by providing these essential products to the varied needs of companies operating in various sectors such as the chemical, oil and gas, pharmaceutical, food and many others. With extensive expertise and experience, the company is known for its commitment to quality and reliability.


Image by Freepik
Syveco offers various industrial valves and fittings that meet the correct price-quality ratio for your needs. The company provides reliable, durable, high-performance products for high-pressure applications, corrosive environments or severe operating conditions. Syveco is committed to offering a wide selection of products from leading manufacturers and providing personal customer service.
We are ready to meet your daily needs and become your preferred project partner.
What to choose between pneumatic and electric actuation?
Syveco supplies both pneumatic and electric actuated valves.
What is a pneumatic actuated valve?
A pneumatic valve is a type of valve that operates with an actuator powered by compressed air. It automatically controls the flow of various fluids such as air, water, steam, corrosive liquids, and petroleum products.
The pneumatic actuator uses compressed air to move the rack, and pinions carrying the valve stem. The rotation of the stem moves the closing element, which opens or closes the fluid passage.
Pneumatic valves are commonly used in industrial applications such as water treatment, food, agricultural, chemical and petrochemical industries requiring high accuracy and reliability.
In explosive environments, pneumatic actuators offer the advantage of not generating sparks or heat, eliminating the risk of fire or explosion. Additionally, pneumatic actuators possess a power-to-weight ratio that surpasses that of electric motors by 5 to 6 times. This characteristic makes them ideal for situations where space is at a premium. However, this type of installation is noisy and it is difficult to achieve precise valve positioning with a pneumatic actuator.


What are the differences between double acting and spring return?
Using a pneumatic system to control actuators offers various possibilities depending on the specific needs. Two common types of pneumatic actuators are spring return and double acting actuators.
In the case of a double-acting actuator, a solenoid pilot valve 5/2 is required for control. Pressure to one of the two chambers of the actuator opens the valve, while pressure to the other chamber creates the opposite action. Thus, the torque generated can vary depending on the pressure and the actuator's size. However, it should be noted that the actuator remains in its current position despite a lack of air.
Spring return actuators operate slightly differently. They use return springs to create the reverse action when the pressure in one of the chambers opens the valve. In the event of a lack of air, the actuator assumes a known position due to the force of the return springs. The torque value here also depends on the size of the actuator, as well as the strength of the springs used. For the control of spring return actuators, a solenoid pilot valve 3/2 is required.
What is an electric actuated valve?
Electric actuated valves are used for automated network sectioning. Valves can therefore be controlled and monitored remotely.
The motor uses electrical energy to operate the valve, which can be opened or closed, and regulate the flow of water or air, etc.
The electric actuator does not support a high number of operations per minute, and is not suitable for high speeds: the operating conditions must be respected.
To motorise a multi-turn valve, only the electric actuator is suitable. This technology applies to gate, knife gate and globe valves.
What is a solenoid valve?
A solenoid valve is a type of electrically operated valve. It can be used to control the flow of liquids or gases in various applications by opening or closing a passage to allow or stop the passage of fluid. A solenoid valve is a small globe or diaphragm valve operated by an electromagnet. It is a simple and compact solution, but limited in diameter. It is only suitable for clean fluids and causes significant pressure drops.
Solenoid valves are commonly used in industrial automation, fluid control, heating and cooling, and safety systems.
What are the differences between electric and pneumatic valves?
|
Actuation with pneumatic actuator |
Actuation with electric actuator |
|
Requires compressed air, and therefore the installation of a compressor |
Requires electricity |
|
Economic solution |
More expensive in standard diameters |
|
Instant operation |
Slower operation |
|
Very high reliability |
Sensitive electronics |
|
Easy safety position |
Complex safety position |
|
Simple ATEX version |
Expansive ATEX version |
The choice between pneumatic or electric actuation depends on the type of energy available, the operating conditions (environments, fluids, intermittent or continuous service, etc.) and the type of valve. Pneumatic valves will be suitable for chemical applications, explosive atmospheres, wet environments or high duty services. An electric valve is ideal for large-diameter piping systems, multi-turn valves and intermittent operations.
Atex
ATEX is the abbreviation for "ATmosphères EXplosives".
Directive 2014/34/E.U., also known as the ATEX Directive, is a European directive that establishes safety and health requirements for equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres, such as production and storage sites for gases, flammable liquids, environment with dust and fibres.
The ATEX Directive was developed in response to an increase in the number of explosions at industrial sites in Europe. It replaced the previous ATEX Directive 94/9/EC in April 2016.
The C.E. marking identifies protective equipment and systems complying with the 2014/34/E.U. directive. A declaration of conformity must accompany them to prove compliance with the directive's requirements.
Read more about the


Manual valves and the ATEX zone |
|
Actuated valves and the ATEX zone |
|
Manual valves do not fall within the directive's scope: simple mechanical products with no ignition source. The electrostatic risk generated by the fluid flow is not a source of ignition specific to the valve. |
Actuated valves are fully within the scope of the directive. | |
|
They can be used in ATEX zones 1, 2, 21 and 22 by the manufacturer's instructions, and if electrostatic continuity is ensured. |
|
It is the assembly that is certified. |
|
The "EX" marking is not permitted. |
|
The assembly of ATEX-compatible/certified components does not automatically imply that the whole unit is certified. |
|
The issue of a declaration of conformity with the directive is not permitted. |
Through our ISO 9001-certified Sectoriel motorisation centre, we offer actuated valve assemblies that comply with ATEX regulations (to request when ordering). |
Oil & Gas
"Oil & Gas" covers the entire oil and gas industry, from exploration and transport to refining.
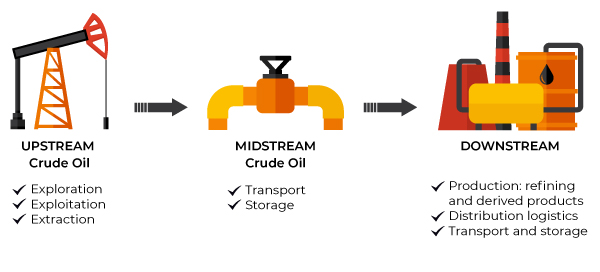

Syveco offers specific ranges for the downstream oil and gas industry, including refining, logistics, transport and storage.
- Our threaded and welding ball valve range includes and 3-piece body ISO pad fire safe.
- Our RF ANSI150 and ANSI300 flanged ball valves range includes and
- You'll also find and , or including ball, check, gate, and globe valves.
OIL & GAS glossary
Firesafe: As a standard, a "fire-safe" valve has a specific construction that guarantees fire-tightness. It must remain watertight and operable when exposed to fire. This is made possible by adding graphite seals in the body and stuffing box.
ATmosphère EXplosive standard, ATEX Zone product is a product compatible without being a potential source of ignition (manual valve excluded). Zones are classified according to danger. Environments where there is a risk of explosion: fuel, gas, combustibles, dust, etc.
NACE:National Association of Corrosion Engineers. NACE standard guarantees anti-corrosion surface treatment. It is sometimes required for aggressive environment, particularly with H2S (hydrogen sulphide). There is no specific certificate. It is mentioned on the 3.1 certificates.
Fugitive Emissions (USA) and TA LUFT (Germany):The Fugitive Emissions (ISO 15848 or API 622) or TA Luft certifications follow different approaches to reduce emissions into the atmosphere, thus guaranteeing a high level of leak tightness, the leak rate is controlled.
Safety Integrity Level is an International standard giving the safety integrity level of an electrical or electronic product. The level of risk reduction is expressed in 4 groups (SIL 1 to SIL 4).
ANSI: American National Standard Institute is an organisation that oversees the development of standards for products, services, processes, systems and employees in the United States.
API: American Petrol Institute is setting standards for the oil industry in the U.S.A. The work units are the inche (NPS) and the psi.
ASTM: American Society for Testing Materials is setting standards organisation for products, materials, systems and services. The same material can be designated in different ways according to DIN or ASTM standards.
API Spec Q1: standard specifying the Quality Management System requirements for organisations supplying products to the Oil & Gas industry.
TRIM: designates the materials used for the seat, stem, bushing, disc or wedge.
What is TRIM?
TRIM refers to the valve's removable and replaceable internal parts in contact with the fluid seat/obturator/stem/gland, for example. The API has standardised TRIM materials by assigning a unique number to each set.
The TRIM available from our range:
TRIM 1: general service, petroleum and petroleum vapours, unsuitable for erosive or corrosive service, -100/+320°C. Steam, gas and standard service up to 370°C. Oil & Steam 480°C
TRIM 5: slightly erosive & corrosive high-pressure service. Excellent for steam and high-pressure water -265/+650°C
TRIM 8: universal TRIM for "standard" service requiring long life. Similar performance to Trim 5 pressure & corrosion. Steam, gas and standard 540°C. Standard TRIM for gates valves
TRIM 10: resistance to corrosive medias at high temperatures and suitable for service at low temperatures
TRIM 12: similar to TRIM 10 for medium pressure and more corrosive or abrasive service
TRIM 16: similar to TRIM 10, more erosive service and higher pressure
Compressed air
When air is pressurised above atmospheric levels using a compressor, it is known as compressed air. This high-pressure air possesses the advantage of being a potent energy source. Due to its versatility, compressed air is extensively utilised as an energy supply.
Compressed air is used in metal, plastics and rubber, food, pharmaceutical, chemical, petrochemical, and automotive industries.
Why use compressed air treatment equipment?
Proper air treatment and filtration are essential to ensure the provision of clean and dry compressed air, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of your equipment. Contaminants that need to be addressed include water, dirt particles, oil, micro-organisms, rust, and deposits in compressed air pipes. These contaminants have the potential to cause blockages, increased wear and tear, malfunctions in pneumatic equipment, corrosion, and the growth of bacteria. By effectively managing air treatment and filtration, you can mitigate these risks and enhance the performance and durability of your equipment.
We offer a range of accessories for compressed air networks. You will find air treatment equipment with filters, lubricators, and regulators. Several spare cartridges have different grades:
-
Pre-filtration grade X3, 3 µm
-
Micronic filtration grade X1, 1 µm
-
Submicronic filtration grade XA, 0.01 µm
These cartridges are used to separate the droplets of water and oil, tiny particles of dirt and micro-organisms. Choose the fineness of filtration following the type of contaminants you need to filter.
-
Active carbon filtration grade XAC, 0.003 mg/m3 is used to remove oil vapour
We also offer drain valves and ball valves specifically suitable for compressed air.




