Local Storage seems to be disabled in your browser.
For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Local Storage in your browser.
WATER INDUSTRY
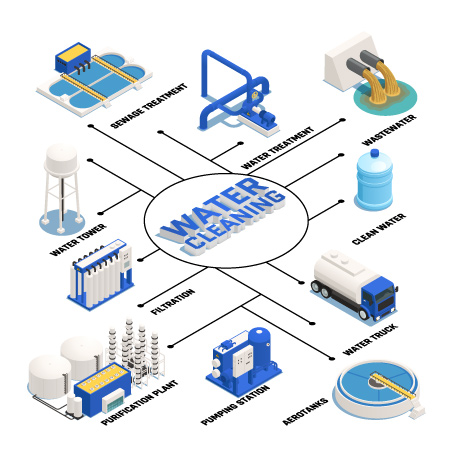
The water industry for human consumption and activities follows a multi-stage process.
- First, there is the production of drinking water, which begins with catchment, also known as pumping or extraction. Catchment involves collecting water from a source. The catchment may be superficial or underground.
- Next comes water treatment, a crucial stage in making water drinkable.
- Water supply is the term used to describe all the pipes that carry treated water to storage tanks.
- Drinking water distribution refers to transporting the water from the storage tanks to the places where it is consumed.
- Finally, the use of water results in the production of wastewater. The purpose of wastewater treatment is to collect, evacuate, treat and discharge wastewater.



What makes up a water distribution network?
Water for human consumption comes from various sources, including groundwater, lakes, rivers and water reservoirs. This water is caught and transported to treatment plants, where it is purified. The necessary pressure is generated either by gravity or by pumping stations. Once treated, the water is pumped into the distribution network to reach consumers (residential or public buildings, businesses, and industry). This network may be made up of ductile iron, PVC, steel or polyethylene (PE) pipes.
A distribution network generally operates at relatively low pressure, although this can vary from one point to another within the same network.
The pressure must be high enough to reach the consumers at the highest points in relation to the pumping station. The network uses pressure reducers or boosters to reduce or increase the water pressure as required. The choice between gate valves and butterfly valves often depends on historical considerations or the design of the network. It can also be influenced by the application and the ability to withstand different pressure ranges.
Syveco offers a wide range of valves and accessories designed to meet the conditions and requirements of water distribution networks: , , , , , ,
How does wastewater treatment work?
It exists several types of wastewaters:
- Greywater from showers, baths, hand basins, washing machines, and kitchens
- Blackwater from toilet flushing and food fixtures
- Sewage greywater, blackwater and trade waste
- Industrial wastewater
After the water is used in domestic, public or industrial activities, it becomes wastewater, which needs to be treated before being safely returned to the environment. In some areas, surface water (rainwater) and sewage mix together before undergoing treatment at sewage works. Nowadays, many new systems separate the two.


The wastewater management process involves several stages. First, the wastewater is transported through a network of pipes and sewers to wastewater treatment plants. These plants are responsible for cleaning and filtering the wastewater.
The initial stage of treatment involves screening the wastewater to remove large objects that could block equipment, cause damage, or pollute rivers.
Next, primary treatment occurs, where organic solid matter is separated from the water. Settlement tanks allow the solids to sink to the bottom while the cleaner water is recovered. The settled solids, referred to as sludge, are then removed for further treatment while the water proceeds to the next stage.
In the secondary treatment stage, the wastewater is introduced into aeration lanes, where air is pumped in to encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria. These bacteria break down and consume harmful substances, leading to their elimination.
After secondary treatment, the wastewater passes through a settlement tank once again. The remaining sludge is recycled back to the secondary treatment stage. The clean water goes through a sand filter system to capture any remaining particles.
The sludge collected could be treated to produce energy (thermic use or biogas installation). The remaining waste, produced after energy generation, is used by recycling to agricultural land as fertiliser.
Once the wastewater has been thoroughly treated, it is safely returned to local rivers, streams or sea. This step is crucial for maintaining water flow and supporting aquatic ecosystems. The quality of the cleaned wastewater is regulated to ensure compliance with high-quality standards.
Wastewater management is a complex process that involves multiple stages and technologies to ensure the safe treatment and disposal of used water.
Syveco offers a range of valves and fittings suitable for wastewater recovery and treatment, such as , , , ,







